What is Bus Topology?
Bus Topology is a Network Topology, in which network nodes are arranged in a linear format, with each node connected directly to the one main network cable with a T-Connecter or tap. The main Network cable is also known as a Trunk, Segment, or Backbone. The main network cable segment must have a terminator installed at both ends of the Bus Topology. This will absorbs the signal when it reaches the end of the wire. If there is no terminator, the electrical signal bounces back at the end of the wire, which causing a collision in the network.
A Bus is a Passive Topology, the data signal passes by the node, not through the node. This means the nodes on the Bus are not responsible for regenerating the data signal.
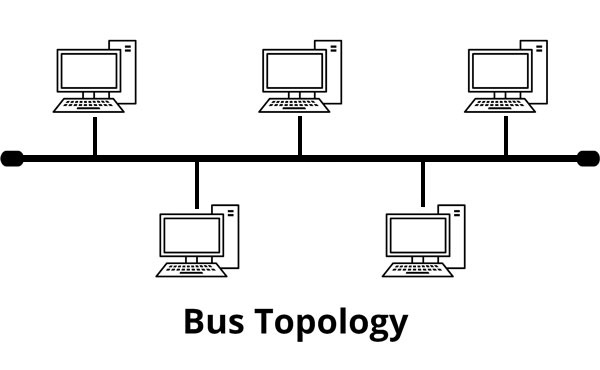
When a node or computer sends out a data signal, it travels the Trunk in both directions from the sender. When the data signal reaches the end of the trunk, it bounces back and returns in there direction it comes from. This is called Signal Bounce. At the time of Data Bounce, if another signal is sent on the trunk, two data signals will collide and be destroyed. To avoid this problem the solution is Terminator, installed at each end of the trunk. The function of the terminator is to absorb the data signal when it reaches the end and prevents the Data Bounce. If there is no Terminator or break in the trunk, because of the unterminated ends, the entire network will go down.
Advantages And Disadvantages of a Bus Topology
Bus Topology is also known as Line Topology, is very easy to set up and requires no additional hardware such as a hub or switch.
So far we describe bus topology, now let’s look at the advantages And disadvantages of a Bus Topology.
Advantages of a Bus Topology
Easy to setup. With a Bus network, simply connect the nodes in a linear format without affecting any other Node.
Bus Network Uses Less cable than Star Topology and Mesh Topology.
You do not need to purchase any additional devices, i.e. Switch or Hub.
Overall Cost is less than other Network Topology, as less Cable and no Central device required.
If a node fails, the network stays functional.
Disadvantages of a Bus Topology
In case of a break in a trunk, the entire network goes down.
If the entire Network goes down, troubleshooting will be very difficult.
Bus Topology is not very Scalable and not suitable for large networks.
Stay Connected & Keep Learning!
Did you find our articles and tutorials helpful? Stay updated with more expert tips—Follow us on Facebook and Instagram!
Be Part of a Global Tech Network! Join our Official Facebook Group for live Q&A, discussions, and networking with a global tech community!



Pingback: Star Topology - Advantages And Disadvantages of a Star Topology - Ofbit.Org